Journal Review in 3 lines: Vuno Published Journal Papers in Lung CT A.I.
[Since 2023]
1. Park, Doohyun, et al. "Development and validation of a hybrid deep learning–machine learning approach for severity assessment of COVID-19 and other pneumonias." Scientific Reports 13.1 (2023): 13420.
[Since 2022]
2. Park, Sohee, et al. "Application of computer-aided diagnosis for Lung-RADS categorization in CT screening for lung cancer: effect on inter-reader agreement." European Radiology (2022): 1-11.
[Since 2021]
3. Ahn, Yura, et al. "Use of a commercially available deep learning algorithm to measure the solid portions of lung cancer manifesting as subsolid lesions at CT: comparisons with radiologists and invasive component size at pathologic examination." Radiology 299.1 (2021): 202-210.
4. Park, Sohee, et al. "Deep learning–based differentiation of invasive adenocarcinomas from preinvasive or minimally invasive lesions among pulmonary subsolid nodules." European Radiology 31 (2021): 6239-6247.
5. Park, Sohee, et al. "Computer-aided detection of subsolid nodules at chest CT: improved performance with deep learning–based CT section thickness reduction." Radiology 299.1 (2021): 211-219.
- 연구 목적(Research Purpose): CT section Thickness에 따라 CAD(Computer Aided Diagnosis)의 SSN(subsolid nodules) 검출 성능을 비교해보고, 딥러닝 기반의 super-resolution 기술을 적용하여 CT section Thickness를 변화시켰을 때 검출 성능이 향상되는지를 확인하는 것이 연구 목표이다.
- 연구 방법(Materials & Methods): Lung CT 영상은 thick setction에 따라 각각 1, 3, 5mm 영상들을 모두 가진 환자들의 데이터를 모았으며(SSN은 6~30mm 이내의 결절들만 ground-truth로 레이블링), 각 thick setction에 따라 CAD로 검출을 시키고 추가로 3, 5mm thickness 영상들은 1mm thickness로 super-resolution 시킨 후에 한번 더 CAD로 검출시켰다.
- 연구 결과(Results & Conclusion): CAD로 검출하여 성능을 비교해본 결과, 1mm thickness에서 SSN 검출 성능이 가장 뛰어났으며(part-solid보다는 nonsolid nodules에서 특히 성능 차이가 컸음), 딥러닝 기반의 super-resolution 알고리즘을 적용하자 3, 5mm thickness 영상의 CAD 성능도 향상되는 것을 확인하였다.
Park et al., 2021, Computer-aided Detection of Subsolid Nodules at Chest CT: Improved Performance with Deep Learning-based CT Se
# 세줄 요약 # 목적: CT section Thickness에 따라 CAD(Computer Aided Diagnosis)의 SSN(subsolid nodules) 검출 성능을 비교해보고, 딥러닝 기반의 super-resolution 기술을 적용하여 CT section Thickness를 변화시켰을 때 검출
pulsar-kkaturi.tistory.com
[Since 2019]
6. Park, Sohee, et al. "Deep learning algorithm for reducing CT slice thickness: effect on reproducibility of radiomic features in lung cancer." Korean journal of radiology 20.10 (2019): 1431-1440.
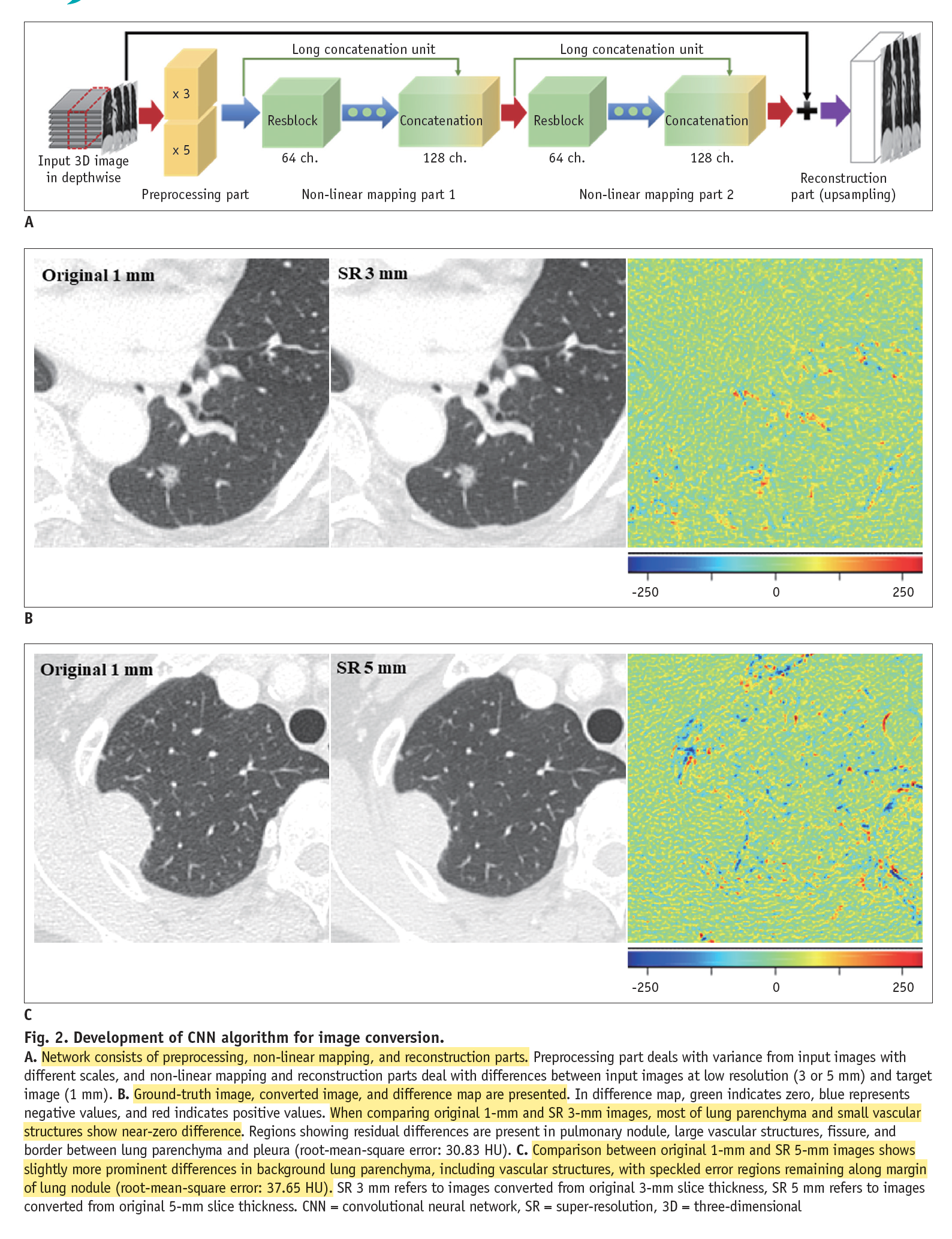
- 연구 목적(Research Purpose): 폐암의 영상학적 특징(Radiomic features; RFs)이 CT Slice Thickness에 따라 잘 나타나는지 확인한 후에, 딥러닝의 기반의 합성곱 신경망(Convolutional Neural Network; CNN)을 사용한 초해상도(Super-resolution; SR) 알고리즘이 CT Slice Thickness를 복원했을 때 RFs도 함께 잘 재현되는지를 확인하고자 한다.
- 연구 방법(Materials & Methods): 데이터셋은 후향적으로 2017년 7월~12월 사이의 병리학적으로 판독된 폐암을 가진 폐 CT 영상 100 례를 모았으며, CT Slice Thickness 1, 3, 5mm 각각 모두 수집하였다. 그후 CNN 기반의 SR 알고리즘으로 3, 5mm Slice Thickness 영상은 1mm로 변환하여 100례에서 얻은 총 702개의 RFs (tumor intensity, texture, wavelet)들의 1mm, 3mm, 5mm, SR 3mm(->1mm), SR 5mm(->1mm) Slice Thickness에 따른 각각의 concordance correlation coefficients (CCCs)를 평가하였다.
- 연구 결과(Results & Conclusion): 1mm vs 3mm, 1mm vs 5mm, 3mm vs 5mm 모두 평균 CCCs 지표는 각각 0.41, 0.27, 0.65 (p value < 0.001)로 모두 낮았으며, 재현성이 높은 RFs들도(CCCs > 0.85 넘는 케이스들) 거의 존재하지 않았습니다(각각 3.6%, 1.0%, 21.5%). 그러나 SR 알고리즘 적용 후(SR 3mm: 3->1, SR 5mm: 5->1)에는 평균 CCCs가 0.58, 0.45, 0.72로 모두 상승하였으며, 재현성이 높은 RFs들의 비율 또한 상승하여(각각 36.3%, 17.4%, 36.9%), 폐암의 RFs 재현성을 개선하기 위해 SR 알고리즘을 사용하여 Slice Thickness를 높이는 딥러닝 기술은 효과가 있음을 보였습니다.




댓글